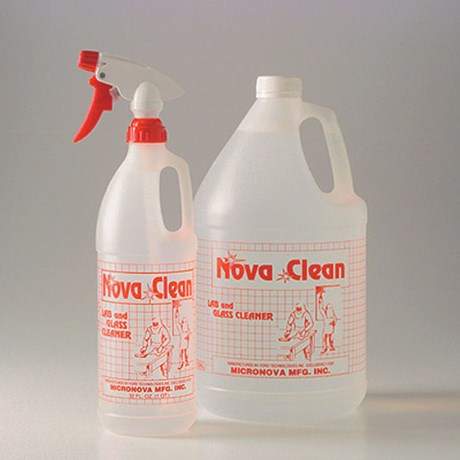
The NovaClean Lab and Glass Clean is a ready-to-use cleaner that has sodium and potassium levels only measurable in parts per million.
The NovaClean Lab and Glass Clean is a ready-to-use cleaner that has sodium and potassium levels only measurable in parts per million.
The low-ionic ready-to-use cleaner is designed for workstations, laminar flow benches, glass, plastic and acrylic screens, cleanroom curtains, and painted surfaces.
Filtered to 0.1 microns, the NovaClean Lab and Glass Clean is available in an easy-to-use quart size spray bottle, while the solution has a good evaporation rate and can be applied directly on the surface to be cleaned. It is also available in gallon containers and filtered to 0.1 microns. The product is low in sodium, bio-degradable, and requires no blending or mixing.